Table 1: Outline of the Article
| Heading Level | Heading Text |
|---|---|
| H1 | The Marvelous World of Aloe Vera |
| H2 | The History and Origin of Aloe Vera |
| H3 | The Importance of Aloe Vera in Ancient Cultures |
| H2 | The Botany of Aloe Vera |
| H3 | The Plant Structure |
| H3 | The Aloe Vera Species |
| H2 | The Nutrient Composition of Aloe Vera |
| H3 | Vitamins and Minerals |
| H3 | Enzymes and Amino Acids |
| H2 | The Health Benefits of Aloe Vera |
| H3 | Aloe Vera for Skin Health |
| H3 | Aloe Vera for Digestive Health |
| H3 | Other Health Benefits |
| H2 | The Uses of Aloe Vera in Everyday Life |
| H3 | Aloe Vera in Cosmetic Products |
| H3 | Aloe Vera in Food and Beverages |
| H2 | Growing Your Own Aloe Vera Plant |
| H3 | Choosing the Right Soil |
| H3 | Watering and Sunlight |
| H2 | Conclusion |
| H4 | FAQs |
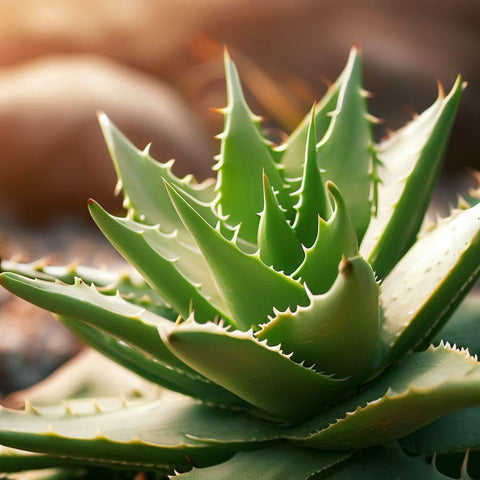
The Marvelous World of Aloe Vera

The History and Origin of Aloe Vera
Stepping back in time, we discover that aloe vera is no newcomer to the stage of natural remedies. Its origins trace back to the Arabian Peninsula, but this wonder plant soon spread to other parts of the world, earning a revered place in many ancient cultures.
The Importance of Aloe Vera in Ancient Cultures
The Egyptians didn't call aloe vera the "plant of immortality" for nothing. Papyrus scrolls dating back to 1550 BC detail the use of aloe vera for various ailments. The plant was so highly regarded that it was considered a funerary gift for pharaohs. It wasn't just the Egyptians, though. The Greeks, Romans, and Chinese also utilized aloe vera for its multitude of benefits.
The Botany of Aloe Vera
Commonly mistaken for a cactus because of its spiky appearance, aloe vera is actually a member of the Liliaceae family, which also includes lilies and onions. Like cacti, though, aloe vera has adapted brilliantly to arid climates, storing large amounts of water in its leaves to survive during droughts.
The Plant Structure
Aloe vera plants are made up of three main parts. The clear gel inside the leaf is the most commonly used part, famous for its soothing properties. The latex, a yellowish substance just beneath the leaf skin, has potent laxative effects. Lastly, the rind, the thickest and toughest part of the leaf, protects the inner contents.
The Aloe Vera Species
Though commonly referred to as just 'aloe vera', the genus Aloe consists of over 500 species of succulent plants. The Aloe vera species, sometimes called true aloe or medicinal aloe, is the most renowned for its health and beauty benefits.
The Nutrient Composition of Aloe Vera
What's in this miraculous plant that gives it so many benefits? Aloe vera is packed with an impressive array of nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and amino acids, each contributing to its various uses and properties.
Vitamins and Minerals
Aloe vera is a good source of vitamins A, C, and E, which are all potent antioxidants. It also contains vitamin B12, folic acid, and choline. Among its mineral content, you'll find calcium, copper, selenium, magnesium, manganese, potassium, sodium, and zinc.
Enzymes and Amino Acids
Aloe vera contains important enzymes like amylase and lipase, which help break down sugars and fats. It also has 20 of the 22 required human amino acids and 7 of the 8 essential ones. This impressive nutritional profile is part of what makes aloe vera such a versatile plant.
The Health Benefits of Aloe Vera
It's clear why aloe vera is often dubbed the "wonder plant." Its nutritional composition alone is enough to impress, but it's how these nutrients work to benefit our health that truly make aloe vera remarkable.
Aloe Vera for Skin Health
One of the most well-known uses of aloe vera is for skin health. The plant's soothing and anti-inflammatory properties help with sunburn, minor cuts, and even chronic skin conditions like psoriasis. The antioxidants in aloe vera can also support skin health by combating the effects of aging.
Aloe Vera for Digestive Health
Internally, aloe vera may support digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements and a healthy gut. The plant's natural enzymes can aid digestion, and its anti-inflammatory properties may soothe and heal the gut lining.
Other Health Benefits
Beyond skin and digestive health, research has suggested other potential benefits of aloe vera, ranging from supporting oral health to possibly improving cardiovascular health. It's also been used traditionally to boost the immune system and reduce joint inflammation. It's important to note, however, that more research is needed to fully understand and validate these benefits.
The Uses of Aloe Vera in Everyday Life
Aloe vera's beneficial properties have made it a popular ingredient in a wide array of products and industries, from beauty and personal care to food and beverages.
Aloe Vera in Cosmetic Products
The soothing and moisturizing properties of aloe vera make it a common ingredient in skincare products, including lotions, creams, and masks. You'll also find aloe vera in many shampoos and conditioners, where it can help nourish and soothe the scalp.
Aloe Vera in Food and Beverages
Many health drinks and juices feature aloe vera as a key ingredient, touting its potential digestive benefits. Aloe vera gel can also be used in cooking, adding a unique texture and health boost to a variety of dishes.
Growing Your Own Aloe Vera Plant
Given its numerous benefits, you might be considering growing your own aloe vera plant. The good news is, aloe vera is relatively easy to grow indoors, and with the right care, you can have a thriving plant that's also a handy natural remedy.
Choosing the Right Soil
Aloe vera is a succulent, and like all succulents, it thrives in well-draining soil. A mix designed specifically for cacti and succulents will be ideal. If you want to create your own, you can mix equal parts of sand, potting soil, and perlite or pumice for a well-draining substrate.
Watering and Sunlight
Aloe vera plants are drought-tolerant and actually prefer to be on the dry side. It's important to let the soil dry out completely between waterings to prevent root rot. As for sunlight, aloe vera likes bright, indirect light. A west or south-facing window would be ideal. Be cautious of too much direct sunlight, though, as it can scorch the leaves.
Conclusion
Aloe vera, the "plant of immortality" to ancient Egyptians, has indeed proven its timeless value. With its rich history, wide-ranging benefits, and numerous applications in everyday life, it's clear why aloe vera continues to be revered in modern times. Whether you use it for skin care, digestive health, or simply enjoy its presence as a houseplant, aloe vera has something to offer everyone.
FAQs
-
Can I use aloe vera directly from the plant?
Yes, you can cut a leaf from a mature aloe vera plant and use the gel directly on your skin. Be sure to wash it first to remove any latex residue, which can be irritating. -
Is it safe to ingest aloe vera?
Aloe vera juice is safe to ingest in moderation, but it's recommended to consult with a healthcare professional first, particularly if you have any medical conditions or are taking medication. -
How often should I water my aloe vera plant?
Generally, watering once every 2-3 weeks is sufficient. The soil should completely dry out between waterings. -
Can aloe vera grow outside?
Aloe vera can grow outside in zones 10-12. In colder climates, it can be grown outdoors in the summer but should be brought inside when temperatures drop. -
Can I use aloe vera for my pet's skin?
While aloe vera is safe for human use, it can be toxic to pets if ingested. It's best to consult with a vet before using aloe vera on your pet.





























Comments (0)
There are no comments for this article. Be the first one to leave a message!